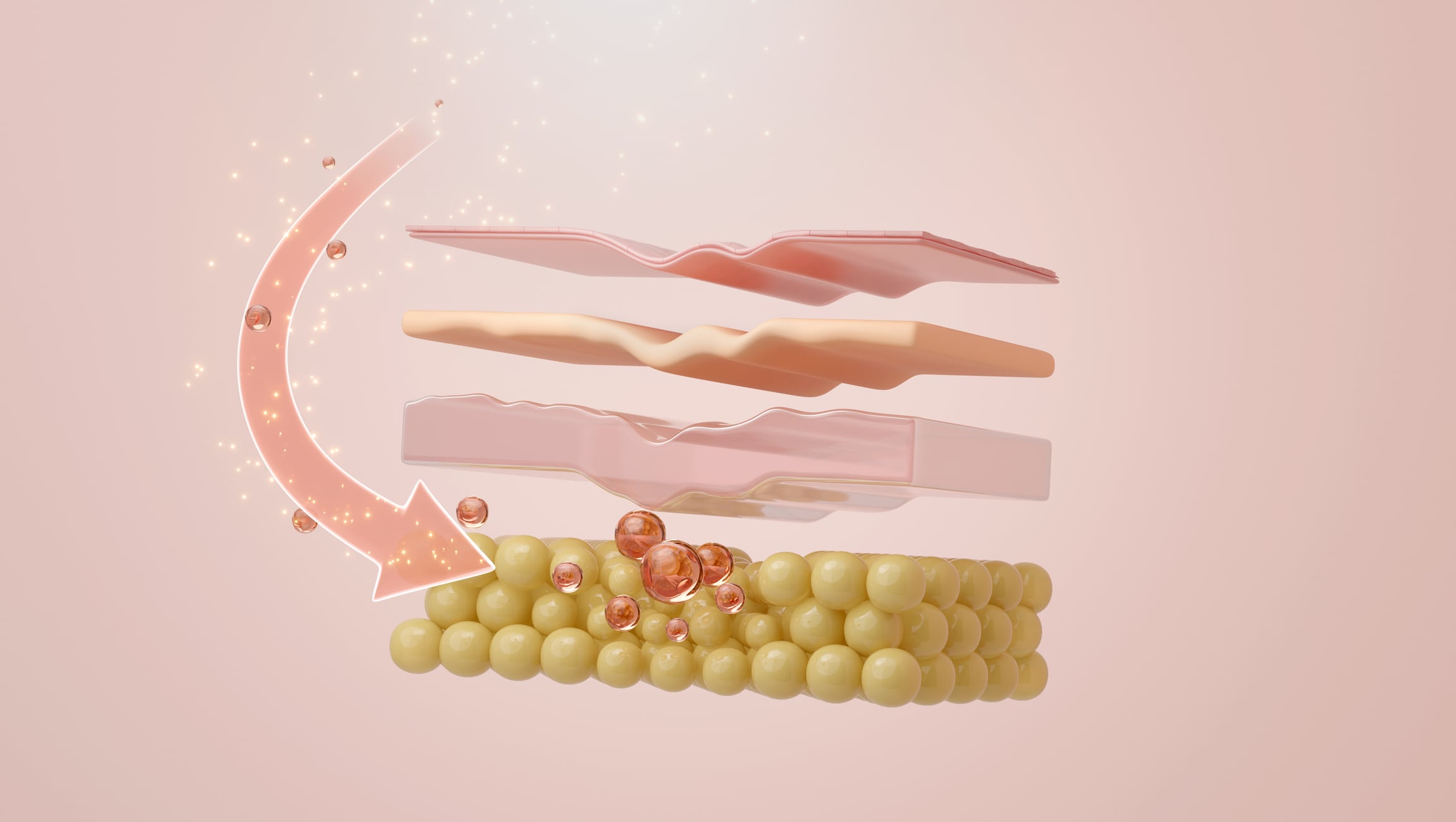
The research team, representing Inha University Hospital, Humantest Co, and B&B Korea, showed how a novel “elastosome” formulation significantly outperformed traditional liposomes by using a flexible membrane that could squeeze through the skin’s microscopic gaps.
This breakthrough addresses a long-standing hurdle for cosmetic formulators who struggle to make bioactive proteins like epidermal growth factor (EGF) effective in topical creams.
The researchers focused on the challenge of the stratum corneum. This outermost layer of the skin acts as a tightly packed lipid barrier that often blocks beneficial molecules from reaching the deeper layers where they are most effective.
While the industry has relied on liposomes for decades to encapsulate active ingredients, these vesicles are often too rigid to penetrate deeply.
To overcome this, the team engineered EGF FLEXIR-SOME particles. These elastosomes consist of a lipid bilayer surrounding a water-friendly core, made highly flexible through the addition of specialised surfactants.
A traditional liposome can be likened to a rigid tennis ball and an elastosome a soft stress ball. This extreme deformability allows the vesicle to change its shape as it moves through the skin.
According to the scientists, this highly flexible vesicle can easily pass through the microscopic gaps within the stratum corneum, which significantly improves the transdermal delivery of encapsulated ingredients.
The final formulation combined 50ppm of EGF with 5% dexpanthenol and nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) to create a multifunctional anti-ageing platform.
Technical stability for commercial manufacturing
The technical specifications of the new delivery system suggested a high level of stability and efficiency for commercial use.
Using a high-pressure microfluidizer operating at 1,000 bar, the team produced particles with an average diameter of 124.8 nanometres. This is the ideal size for cosmetic applications, as it is small enough to be effective but large enough to remain stable.
Furthermore, the zeta potential — a key measurement of how well particles stay spread out without clumping together — was measured at -57.53mV. This was a significantly stronger charge than the -45.08mV seen in conventional liposomes, indicating that the elastosome formulation would be much more stable over time and less likely to separate in the bottle.
Proven penetration in lab testing
One of the most compelling findings is the dramatic difference in skin penetration speed.
The researchers used dexpanthenol as a marker to track how well the system worked. In laboratory tests using an artificial skin membrane that mimicked human skin, the elastosome formulation showed detectable penetration within six hours.
The intensity of the absorption continued to increase throughout the 24-hour test period.
In striking contrast, the control group using standard liposomes showed no detectable absorption at all, even after extended periods. This suggested that the elastosome technology was not just a marginal improvement but a fundamental shift in delivery capability.
Clinical results show younger looking skin
The team then moved to clinical trials to see how these lab results translated to real-world skin health. They recruited 22 healthy Korean women over the age of 30 for a two-week split-face study, where different concentrations were tested on each side of the face.
Participants applied a 2% elastosome cream to one side and an 8% version to the other.
The results showed that even the lower 2% concentration (equivalent to 1ppm of EGF) delivered substantial improvements. In 14 days, eye area elasticity increased by 9.87% and wrinkle depth decreased by 8.97%.
The clinical data also highlighted significant improvements in skin lifting and overall skin age. The researchers used a specialised formula to calculate a Skin Age Index based on three factors: elasticity, roughness and sagging.
For those using the 2% formulation, the skin age index dropped from 39.47 to 33.86, indicating a 14.21% improvement. The 8% formulation also performed well, showing a 10.49% improvement.
Results of the 2% concentration suggested that the elastosome delivery system could be efficient enough to reach a biological saturation point quite quickly.
Massive gains in hydration and barrier repair
Beyond anti-ageing, the study confirmed that the formulation was a powerhouse for hydration and repairing damaged skin.
In a separate test involving 21 women, a single application of the cream increased skin moisture by 448.52%. This was measured using skin permittivity, a way to track water content on the skin surface.
The study also found that the cream improved transepidermal water loss (TEWL) by 31.57% after the skin was irritated, compared to a 10.59% improvement in the control group.
Hyperpigmentation and melasma also saw a reduction during the trial. After two weeks of twice-daily use, the melanin content on the subjects’ cheeks decreased by 7.89%.
The researchers stated that this combined effect facilitated the deep and effective delivery of essential components like EGF and NMN, which amplified the overall benefits to the skin.
Additionally, the study included rigorous primary skin irritation tests on 32 subjects. Both the 2% and 8% formulations received a perfect safety score, which led the researchers to classify them as non-irritants with no reported side effects or allergic reactions.
Future outlook for the EGF platform
While the results were promising, the researchers acknowledged some limitations that could provide a roadmap for future development. They noted that because the 2% and 8% concentrations performed similarly, the 2% dose may have already hit the maximum benefit the skin could absorb in a short window.
As such, future research should involve larger groups and longer-term studies to find the exact “sweet spot” for ingredient concentration. The researchers also recommended testing the formulation on more diverse ethnic populations to ensure the results are universal.
They wrote: “The EGF FLEXIR-SOME formulation significantly improved essential skin parameters, including elasticity, hydration, anti-ageing effects, barrier repair, and pigmentation reduction.
“Collectively, these findings highlight the potential of this advanced elastosome delivery system as a multifunctional cosmetic platform for enhancing the efficacy of potent bioactive ingredients such as EGF, while simultaneously supporting overall skin health.”
Source: Cosmetics
“Development of an Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF) Loaded Elastosome Formulation for Enhanced Skin Penetration and Anti-Aging Effects”
https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics13010010
Authors: Heo Seul Gi, et al.